The Role of Vitamins in a Balanced Diet
The Essential Role of Vitamins in Nutrition
Vitamins are organic compounds that are vital for the proper functioning of our bodies. They play a crucial role in a balanced diet and are essential for various biological processes. Unlike macronutrients like carbohydrates, proteins, and fats, vitamins are required in smaller amounts, yet their impact is significant. A balanced diet rich in vitamins supports immune function, promotes growth and development, and helps cells and organs perform optimally.
Vitamins are divided into two categories: water-soluble and fat-soluble. Water-soluble vitamins include the B-vitamins and vitamin C, which are not stored in the body and need to be consumed regularly. Fat-soluble vitamins, such as vitamins A, D, E, and K, can be stored in the body’s fatty tissues and liver, allowing for less frequent consumption. Each vitamin has specific roles and benefits, making a varied and balanced diet essential.
For example, vitamin C is renowned for its role in boosting the immune system and its antioxidant properties. It helps protect cells from damage and aids in the absorption of iron. On the other hand, vitamin D is crucial for bone health as it helps in the absorption of calcium. Without adequate vitamin D, bones can become thin and brittle. These examples highlight the diverse roles that vitamins play in maintaining health and preventing disease.
- Water-soluble vitamins: B-vitamins, Vitamin C
- Fat-soluble vitamins: Vitamins A, D, E, K
Understanding the Sources of Vitamins
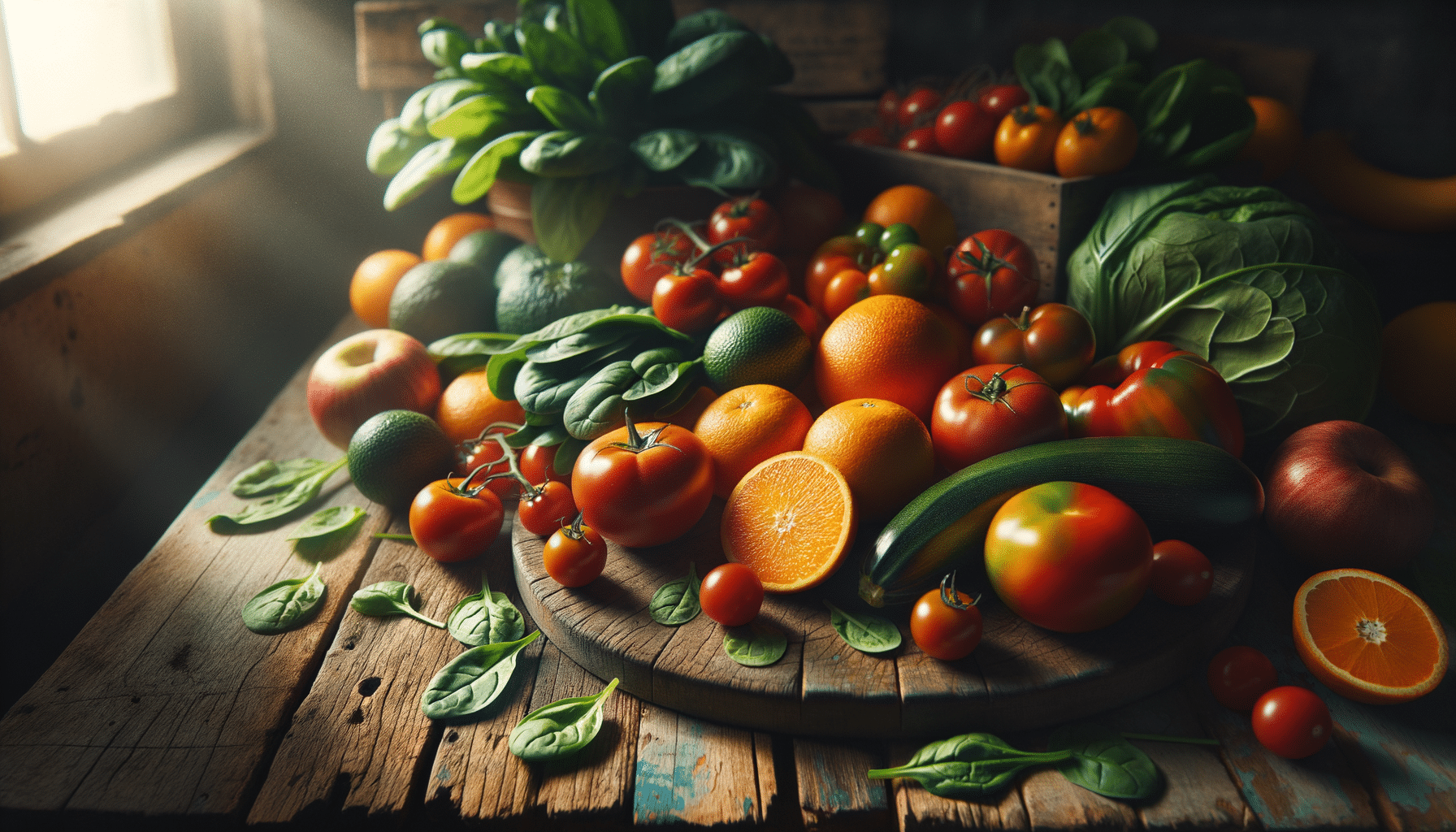
Obtaining vitamins from dietary sources is the most effective way to ensure adequate intake. A diverse diet that includes a variety of fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains typically provides all the vitamins necessary for good health. Each food group offers specific vitamins, and understanding these sources can help in planning a balanced diet.
Fruits and vegetables are particularly rich in vitamins. For instance, citrus fruits like oranges and lemons are excellent sources of vitamin C. Leafy greens such as spinach and kale provide a significant amount of vitamin K, which is essential for blood clotting and bone health. Carrots and sweet potatoes are high in beta-carotene, which the body converts into vitamin A, supporting vision and immune function.
Animal-based foods also contribute to vitamin intake. Dairy products and eggs are rich in vitamin D and B12, which are crucial for bone health and nerve function, respectively. Fish, especially fatty varieties like salmon and mackerel, are not only high in vitamin D but also provide omega-3 fatty acids, which support cardiovascular health.
- Fruits: Citrus fruits (Vitamin C)
- Vegetables: Leafy greens (Vitamin K), Carrots (Vitamin A)
- Animal-based: Dairy (Vitamin D), Fish (Vitamin D and Omega-3)
The Impact of Vitamin Deficiencies
Vitamin deficiencies can lead to a range of health issues, highlighting the importance of a balanced diet. Each vitamin deficiency presents with specific symptoms and health risks, underscoring the need for adequate intake of all vitamins.
Vitamin D deficiency, for example, can lead to bone-related disorders such as rickets in children and osteomalacia in adults, both of which cause bone pain and deformities. Vitamin C deficiency can result in scurvy, a condition characterized by fatigue, gum disease, and skin problems. Moreover, insufficient vitamin B12 can lead to anemia and neurological issues, as it is essential for red blood cell production and nerve function.
Preventing deficiencies requires a mindful approach to diet. Including a variety of vitamin-rich foods can help avoid these health issues. In some cases, supplements may be necessary, especially for individuals with dietary restrictions or specific health conditions. However, supplements should be taken under medical guidance to prevent toxicity or interactions with other medications.
Integrating Vitamins into Daily Meals
Incorporating a wide range of vitamins into daily meals can be both simple and enjoyable. Planning meals that include a variety of food groups ensures a balanced intake of essential nutrients.
Start the day with a breakfast that includes fruits like berries or a citrus fruit, providing a boost of vitamin C. Whole grain cereals or bread can supply B-vitamins and fiber. A lunch consisting of a fresh salad with leafy greens, tomatoes, and avocado not only provides vitamins K and E but also adds healthy fats to the diet.
For dinner, consider a protein-rich dish like grilled chicken or fish, paired with a side of steamed vegetables. This combination offers a range of vitamins, including B-vitamins from the protein source and vitamins A and C from the vegetables. Snacking on nuts or seeds throughout the day can contribute to vitamin E intake, supporting skin health and antioxidant protection.
- Breakfast: Fruits (Vitamin C), Whole grains (B-vitamins)
- Lunch: Leafy greens (Vitamin K), Avocado (Vitamin E)
- Dinner: Grilled chicken or fish (B-vitamins), Steamed vegetables (Vitamins A and C)
Conclusion: The Significance of Vitamins in Health
Vitamins are indispensable to our health, playing pivotal roles in numerous bodily functions. A balanced diet rich in vitamins not only supports physical health but also enhances mental well-being. Understanding the sources and benefits of each vitamin empowers individuals to make informed dietary choices.
While dietary supplements can be beneficial in certain situations, the emphasis should remain on obtaining vitamins from natural food sources. This approach ensures a holistic intake of nutrients, fiber, and other beneficial compounds that supplements alone cannot provide. By prioritizing a varied and nutrient-rich diet, individuals can support their health, prevent deficiencies, and enjoy a vibrant, energetic life.