Nutritional Support for Cognitive Health: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction to Cognitive Health and Nutrition
Cognitive health, a crucial aspect of overall well-being, refers to the ability to think, learn, and remember. It encompasses brain functions such as memory, processing speed, and problem-solving. Maintaining cognitive health is essential as it affects daily life and long-term mental acuity. Nutrition plays a vital role in supporting cognitive health, as certain nutrients can enhance brain function and protect against cognitive decline. This article explores the relationship between nutrition and cognitive health, providing insights into how dietary choices can support brain function.
The Role of Omega-3 Fatty Acids
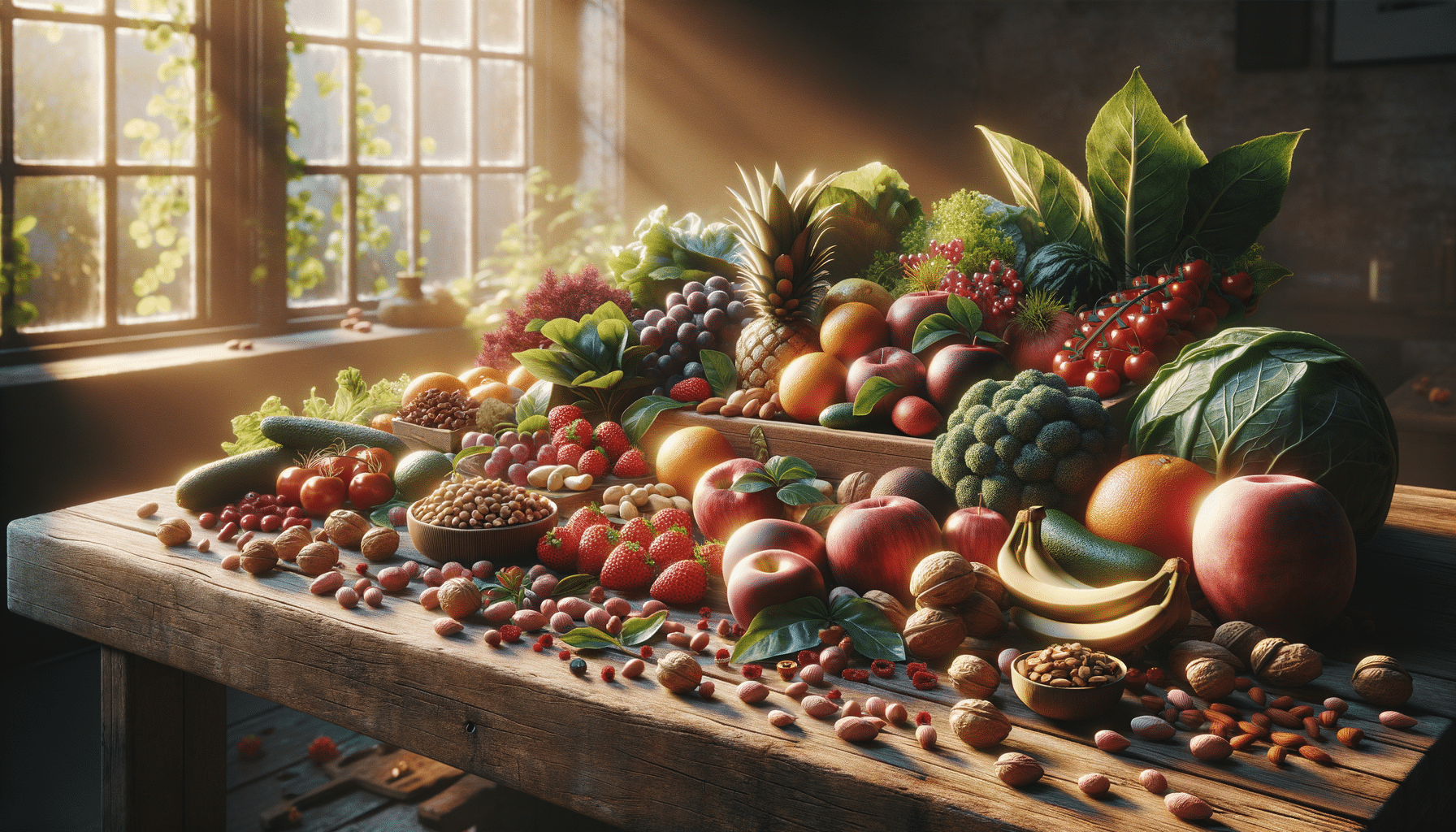
Omega-3 fatty acids, particularly EPA and DHA, are renowned for their cognitive benefits. These essential fats are integral components of cell membranes in the brain. Studies suggest that omega-3s support cognitive functions such as memory and mood regulation. They are found abundantly in fatty fish like salmon and mackerel, as well as in flaxseeds and walnuts. Regular consumption of omega-3-rich foods can help maintain cognitive health and may reduce the risk of neurodegenerative diseases.
Antioxidants and Brain Protection
Antioxidants play a crucial role in protecting the brain from oxidative stress, which can damage cells and contribute to cognitive decline. Vitamins C and E, along with flavonoids found in fruits and vegetables, are powerful antioxidants. These nutrients help neutralize free radicals, thereby reducing inflammation and supporting brain health. Incorporating a variety of colorful fruits and vegetables into your diet ensures a good intake of these protective compounds.
The Impact of B Vitamins on Cognitive Function
B vitamins, including B6, B9 (folate), and B12, are essential for brain health. They are involved in the production of neurotransmitters, which are chemicals that facilitate communication between brain cells. Deficiencies in B vitamins can lead to cognitive impairments and mood disorders. Sources of B vitamins include whole grains, legumes, eggs, and leafy greens. A balanced diet that includes these foods can support cognitive function and mental clarity.
Conclusion: Nurturing the Brain with Nutrition
In conclusion, maintaining cognitive health is a multifaceted endeavor that includes proper nutrition. Omega-3 fatty acids, antioxidants, and B vitamins are just a few of the nutrients that support brain function and protect against cognitive decline. By making informed dietary choices and incorporating a variety of nutrient-rich foods, individuals can enhance their cognitive health and improve their quality of life. Emphasizing a balanced diet rich in these essential nutrients is a proactive approach to preserving mental acuity and overall well-being.